http
http 1.0 http 1.1
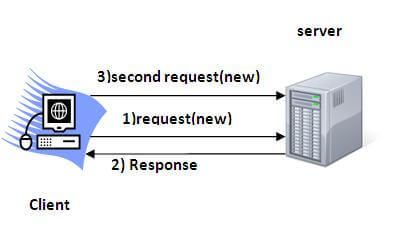
HTTP1.0最早在网页中使用是1996年,那个时候只是使用一些较为简单的网页和网络的请求,每次请求都需要建立一个单独的连接,上一次和下一次请求完全分离。这种做法,即使每次的请求量都很小,但是客户端和服务端每次建立TCP连接和关闭TCP连接都是相对比较费时的过程,严重影响客户端和服务端的性能。
基于以上的问题,HTTP1.1在1999年广泛应用于现在的各大浏览器网络请求中,同时HTTP1.1也是当前使用最为广泛的HTTP协议(2015年诞生了HTTP2,但是还未大规模应用),这里不详细对比HTTP1.1针对HTTP1.0改进了什么,只是在连接这块,HTTP1.1支持在一个TCP连接上传送多个HTTP请求和响应,减少了建立和关闭连接的消耗延迟,一定程度上弥补了HTTP1.0每次请求都要创建连接的缺点,这就是长连接,HTTP1.1默认使用长连接。
那么,长连接是如何工作的呢?首先,我们要明确一下,长短连接是通信层(TCP)的概念,HTTP是应用层协议,它只能说告诉通信层我打算一段时间内复用TCP通道而没有自己去建立、释放TCP通道的能力。
- http的keep-alive和tcp的keep-alive的区别
- http的keep-alive是为了复用已有连接
- tcp的keep-alive是为了保活,即保证对端还存活,不然对端已经不在了我这边还占着和对端的这个连接,浪费服务器资源,做法是隔一段时间发送一个心跳包到对端服务器,一旦长时间没有接收到应答,就主动关闭连接
WebSockets
WebSockets provide a persistent connection between a client and server that both parties can use to start sending data at any time.**
1 | // Create a new WebSocket. |
Once the connection has been established the
openevent will be fired on your WebSocket instance.请求
ws://localhost:9095/webSocket/d72b3660-29a8-4276-9eb1-3373e82fdd92后台请求的结果传入websocket是通过session建立关联的
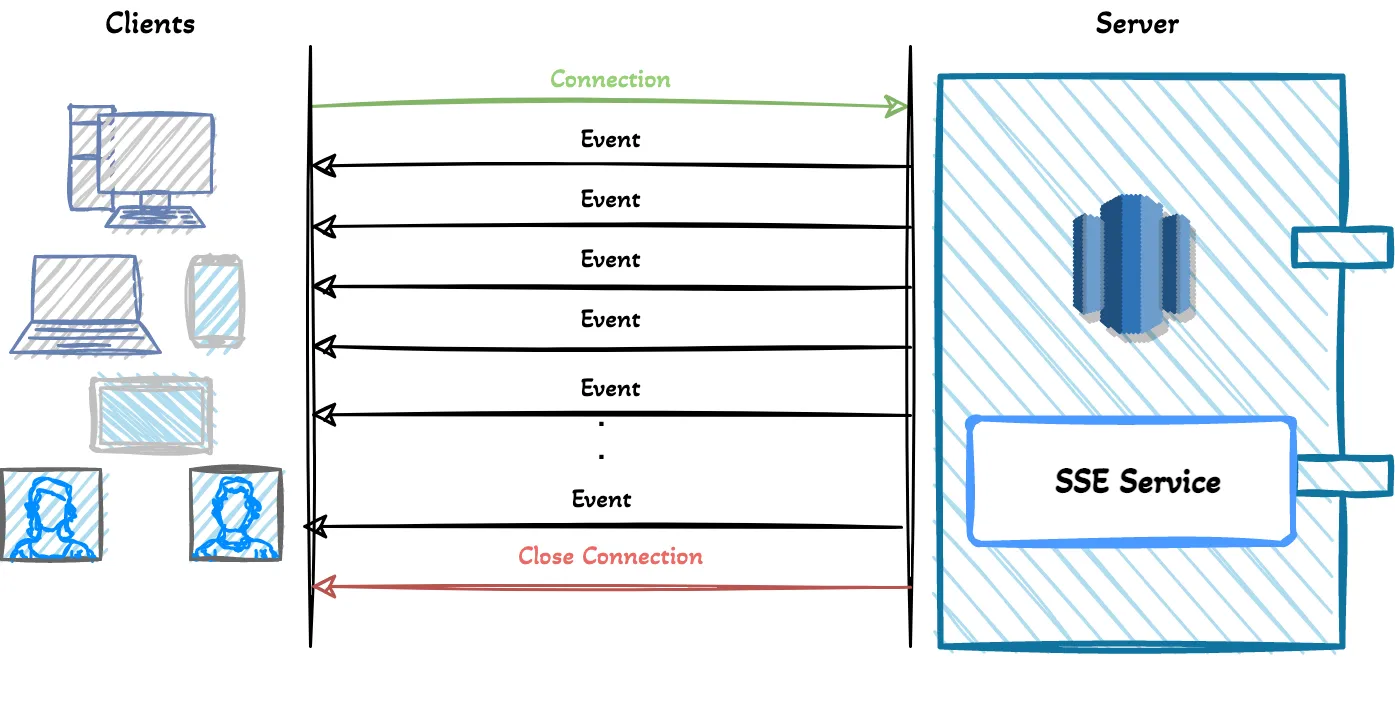
SSE(Server-Sent Events)
client
1 | GET/POST /api/v1/live-scores |
Accept: text/event-streamindicates the client waiting for event stream from the server,Cache-Control: no-cacheindicates that disabling the caching andConnection: keep-aliveindicates the persistent connection. This request will give us an open connection which we are going to use to fetch updates. After the connection, the server can send messages when the events are ready to send by the server. The important thing is that events are text messages inUTF-8encoding.
1 | curl -H "Accept: text/event-stream" -H "Cache-Control: no-cache" -N <SSE_ENDPOINT_URL> |
server
Disadvantages
- One potential downside of using Server-Sent Events is the limitations in data format. Since SSE is restricted to transporting UTF-8 messages, binary data is not supported.
- When not used over HTTP/2, another limitation is the restricted number of concurrent connections per browser. With only six concurrent open SSE connections allowed at any given time, opening multiple tabs with SSE connections can become a bottleneck. (Credit: Dan Messenger)
cookie
- Cookies are text string stored as key/value
- The server Create the cookie and send it to the user’s browser where it’ll be stored.
- The Browser will send that cookie every time it send a request to that server.
1 | HttpOnly: 这个属性用来限制cookie只能通过HTTP(S)协议访问,不能通过客户端脚本(如JavaScript)访问。这主要是为了减少跨站脚本攻击(XSS)的风险,因为攻击者不能通过脚本读取到这些cookie。 |
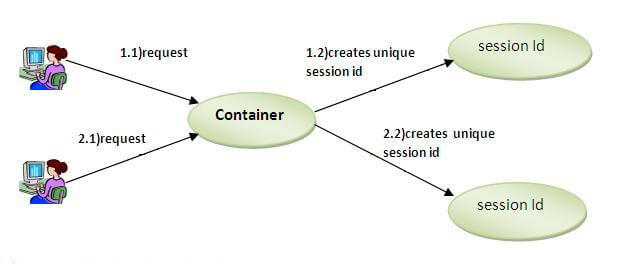
session
- This session is associated with a randomly generated unique ID, which is created by the server. It’s called “session ID”.
- The generated session ID is then sent to the user’s browser and stored as a cookie, while the session data is stored on the server-side.
- Sessions are often used to store sensitive information such as user credentials and financial data. They are more secure than cookies because the information is stored on the server-side and not on the client-side.
ref
html
label
chrome页面跳转,需要使用 i 标签,不能使用 button 标签,因为在button的点击事件中,window.location.href不起作用。(但firefox起作用)
textarea标签里面的属性要紧靠书写,且不要换行,不然,会显示textarea默认赋值为多个空格
1
<textarea type="text"class="form-control"id="obj_address"placeholder="地址(必填)"name="address"isvalid="yes"checkexpession="NotNull"errormsg="地址"></textarea>
css
display
每个元素都有一个默认的 display 类型
不过你可以随时随地的重写它!如常见的例子是:把 li 元素修改成 inline,制作成水平菜单。
p标签是块级元素,span元素是行内元素。内元素可以写在块级元素里面 比如<p><span>内容</span></p>
- block
值为block的为块级元素, 如:p、form、header、footer、section
- inline
值为inline的为行内元素
position
- static
static是默认值,一个static元素表示它不会被”positioned”,一个position属性被设置为其它值得元素表示它会被”positioned”
- relative
relative,在一个相对定位(position属性的值为relative)的元素上设置 top 、 right 、 bottom 和 left 属性会使其偏离其正常位置。
其他的元素的位置则不会受该元素的影响发生位置改变来弥补它偏离后剩下的空隙。
- fixed
fixed,一个固定定位(position属性的值为fixed)元素会相对于视窗来定位,这意味着即便页面滚动,它还是会停留在相同的位置。
和 relative 一样, top 、 right 、 bottom 和 left 属性都可用。
- absolute
absolute, 它与 fixed 的表现类似,但是它不是相对于视窗而是相对于最近的“positioned”祖先元素。
如果绝对定位(position属性的值为absolute)的元素没有“positioned”祖先元素,那么它是相对于文档的 body 元素,并且它会随着页面滚动而移动。
记住一个“positioned”元素是指 position 值不是 static 的元素。
mbp

margin
是设置两个标签的间隔,也就是距离
padding
比如一个p标签,它是100px*100px,我们使用的时候p标签的文字是贴着p标签的最左侧的,想要它的文字距离边界远一点,好看一点,就是需要做一个样式的调整,我们可以用到padding这个属性,假如说设置是10px,就是说这个p标签的大小依然是100px*100px,但是它的内容是变成了90px*90px;
border
boarder是设置边框的意思,他和padding的区别在于,padding是在标签边缘往里缩减,而border是在标签的边缘往外扩展,也就是说是一个100px*100px的标签,我设置他的border为20px,我们就可以看到整个标签的大小是变成了120px*120px,也就是说多出来了120px,其标签的内容也还是100px*100px的
nodejs
版本管理
- 可以用 nvm 进行管理
1 | vue项目: npm run dev 会在开发环境下 立即启动项目 |
jquery
语法
设置标签属性
$("div").attr("属性名","属性值");设置标签样式
$("div").css("color","yellow");或$("div").css("padding-left"))移除属性
$("div").removeAttr("id");遍历数组
原生js有两种方法都可以使用[for(var i;i<arr.length;i++){},for(var i in arr){}]
jquery有两个函数共计四种方法都可以使用
1
2
3
4$.each(arr,function(i,item){}),
$(arr).each(function(i,item){}),
$.map(arr,function(i,item){}),
$(arr).map(function(i,item){})
遍历对象
原生js有一种方法可以使用[for(var i in obj){}]
jquery有两个函数共计两种方法可以使用
1
2$.each(obj,function(i,item){})
$.map(obj,function(i,item){})
Jquery中的ajax在默认不写async情况下,请求为异步请求;即:async:true
$(function(){ })是定义一个匿名函数,它是$(document).ready(function(){})的简写
jpa
What is
Java Persistence API is a collection of classes and methods to persistently store the vast amounts of data into a database which is provided by the Oracle Corporation.
Where to use
To reduce the burden of writing codes for relational object management, a programmer follows the ‘JPA Provider’ framework, which allows easy interaction with database instance. Here the required framework is taken over by JPA.

JPA Pro
JPA is an open source API, therefore various enterprise vendors such as Oracle, Redhat, Eclipse, etc. provide new products by adding the JPA persistence flavor in them. Some of these products include:Hibernate, Eclipselink, Toplink, Spring Data JPA, etc.
Architecture

jpa class relationships

ORM Architecture

Entity Relationships
- @ManyToOne Relation
- @OneToMany Relation
- @OneToOne Relation
- @ManyToMany Relation
session
Session simply means a particular interval of time.
Session Tracking is a way to maintain state (data) of an user. It is also known as session management in servlet.
HTTP is stateless that means each request is considered as the new request. It is shown in the figure given below:
There are four techniques used in Session tracking:
- Cookies
- Hidden Form Field
- URL Rewriting
- HttpSession
cookie
A cookie is a small piece of information that is persisted between the multiple client requests.
A cookie has a name, a single value, and optional attributes such as a comment, path and domain qualifiers, a maximum age, and a version number.
how cookie work

type of cookie
Non-persistent cookie
It is valid for single session only. It is removed each time when user closes the browser.
Persistent cookie
It is valid for multiple session . It is not removed each time when user closes the browser. It is removed only if user logout or signout.
Advantage
- Simplest technique of maintaining the state.
- Cookies are maintained at client side.
Disadvantage
- It will not work if cookie is disabled from the browser.
- Only textual information can be set in Cookie object.
HttpSession Interface
- An object of HttpSession can be used to perform two tasks:
- bind objects
- view and manipulate information about a session, such as the session identifier, creation time, and last accessed time.
DVA
dva = React-Router + Redux + Redux-saga
- 路由: React-Router
- 架构: Redux
- 异步操作: Redux-saga

State
tate 表示 Model 的状态数据
Action
Action 是一个普通 javascript 对象,它是改变 State 的唯一途径。
- action 必须带有
type属性指明具体的行为,其它字段可以自定义,如果要发起一个 action 需要使用dispatch函数;需要注意的是dispatch是在组件 connect Models以后,通过 props 传入的。
dispatch
dispatching function 是一个用于触发 action 的函数
action 是改变 State 的唯一途径,但是action只描述了一个行为,而 dipatch 可以看作是触发这个行为的方式,而 Reducer 则是描述如何改变数据的。
connect Model 的组件通过 props 可以访问到 dispatch,可以调用 Model 中的 Reducer 或者 Effects.
Reducer
Reducer函数接受两个参数:之前已经累积运算的结果和当前要被累积的值,返回的是一个新的累积结果。该函数把一个集合归并成一个单值。
- 在 dva 中,reducers 聚合积累的结果是当前 model 的 state 对象。通过 actions 中传入的值,与当前 reducers 中的值进行运算获得新的值(也就是新的 state)。
Effect
Effect 被称为副作用,在我们的应用中,最常见的就是异步操作。
它来自于函数编程的概念,之所以叫副作用是因为它使得我们的函数变得不纯,同样的输入不一定获得同样的输出。
dva 为了控制副作用的操作,将异步转成同步写法,从而将effects转为纯函数
Subscription
Subscriptions 是一种从 源 获取数据的方法,它来自于 elm。
- Subscription 语义是订阅,用于订阅一个数据源,然后根据条件 dispatch 需要的 action。
数据流图

State 是储存数据的地方,收到 Action 以后,会更新数据。
View 就是 React 组件构成的 UI 层,从 State 取数据后,渲染成 HTML 代码。只要 State 有变化,View 就会自动更新。
Action 是用来描述 UI 层事件的一个对象。
1
2
3
4dispatch({
type: 'click-submit-button',
payload: this.form.data
})connect 是一个函数,绑定 State 到 View。
1
2
3
4
5
6import { connect } from 'dva';
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return { todos: state.todos };
}
connect(mapStateToProps)(App);connect 方法返回的也是一个 React 组件,通常称为容器组件。因为它是原始 UI 组件的容器,即在外面包了一层 State。
dispatch 是一个函数方法,用来将 Action 发送给 State。
被 connect 的 Component 会自动在 props 中拥有 dispatch 方法。
数据流图二

Model 对象的属性
每个model,实际上都是普通的JavaScript对象
namespace: 当前 Model 的名称。整个应用的 State,由多个小的 Model 的 State 以 namespace 为 key 合成
state: 该 Model 当前的状态。数据保存在这里,直接决定了视图层的输出
reducers: Action 处理器,处理同步动作,用来算出最新的 State
effects:Action 处理器,处理异步动。dva 提供多个 effect 函数内部的处理函数,比较常用的是
call和put。- call:执行异步函数
- put:发出一个 Action,类似于 dispatch
subscriptions
restful
- GET: A safe read-only method that reads a single or a list of resources.
- POST: Creates a new resource.
- PUT: Completely replaces the resource(s) at the given location with the new data.
- PATCH: Merges the resource(s) at the given location with the new data.
- DELETE: Deletes the resource(s) at a location.
- HEAD: Same as GET but only returns the header and no data.
用 URL 表示要操作的资源,用不同的 HTTP 请求(GET,POST,PUT,DELETE)描述对资源的操作,通过 HTTP 的状态码来判断此次对资源操作的结果,这就是 Restful风格。
- GET 用来获取资源
- POST 用来新增资源
- PUT 用来更新资源
- DELETE 用来删除资源
- put和delete虽然是http协议的规范 ,但是遗憾的是,所有的无论是html4还是h5都不支持,所以我们在实际开开发过程当中要模拟这两种状态。
Restful有什么意义
- 网络上的所有的信息体都看作一种资源,对网络资源的某种操作,都是通过 method 来确定的。
- 对于现在的数据或者资源提供方,对外透露的接口一般是 restful 风格的,有利于不同系统之间的资源共享,而且只需要遵守规范不需要做另外的配置就能达到资源共享。
restful 是用来外提供接口的,主要用于在不同的系统之间进行数据的交互。
ps:其实在做内部系统的时候并不会使用 restful 风格的 url 请求,只用普通的 @RequestMapping 来匹配请求就行了。
返回码
RESTful API 中的标准返回码通常遵循 HTTP 状态码,并根据不同的操作和结果返回不同的状态码。以下是一些常见的 HTTP 状态码及其通常的含义:
- 200 OK: 表示请求成功。通常用于 GET 请求。
- 201 Created: 表示成功创建了新的资源。通常用于 POST 请求。
- 204 No Content: 表示请求成功处理,但没有返回内容。通常用于 DELETE 请求。
- 400 Bad Request: 表示客户端发送的请求有错误,服务器无法理解。
- 401 Unauthorized: 表示请求需要用户认证,用户没有提供有效的认证信息。
- 403 Forbidden: 表示服务器理解请求,但拒绝执行,通常因为权限问题。
- 404 Not Found: 表示请求的资源不存在。
- 405 Method Not Allowed: 表示请求方法不被允许。
- 409 Conflict: 表示请求可能引发冲突,例如更新资源时的版本冲突。
- 500 Internal Server Error: 表示服务器在处理请求时发生了错误。
- 502 Bad Gateway - This indicates an invalid response from an upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable - This indicates that something unexpected happened on server side (It can be anything like server overload, some parts of the system failed, etc.).
RESTful API 的返回码可以根据实际情况进行适当扩展和调整,但通常遵循以上基本的 HTTP 状态码标准。
TIPS
- url中包含传参时,例如delete /auth/user/{参数},那此时其他delete方法 /auth/user/other,会发生冲突,需要在路径侯后面添加“/”,变成/auth/user/other/
- reference Best practices for REST API design