vCluster is a technology that creates virtual clusters within a physical Kubernetes cluster. These virtual clusters are fully functional and provide enhanced isolation and flexibility for multi-tenancy. Each vCluster operates independently, with its own API server and control plane, while sharing the underlying resources of the host cluster.
Kubernetes serves as the foundational platform for container orchestration, while vCluster enhances its capabilities by providing isolated, virtualized environments for multi-tenant applications. This relationship allows organizations to maximize resource utilization and maintain security across diverse teams and applications
1 | +--------------------------------------------------+ |
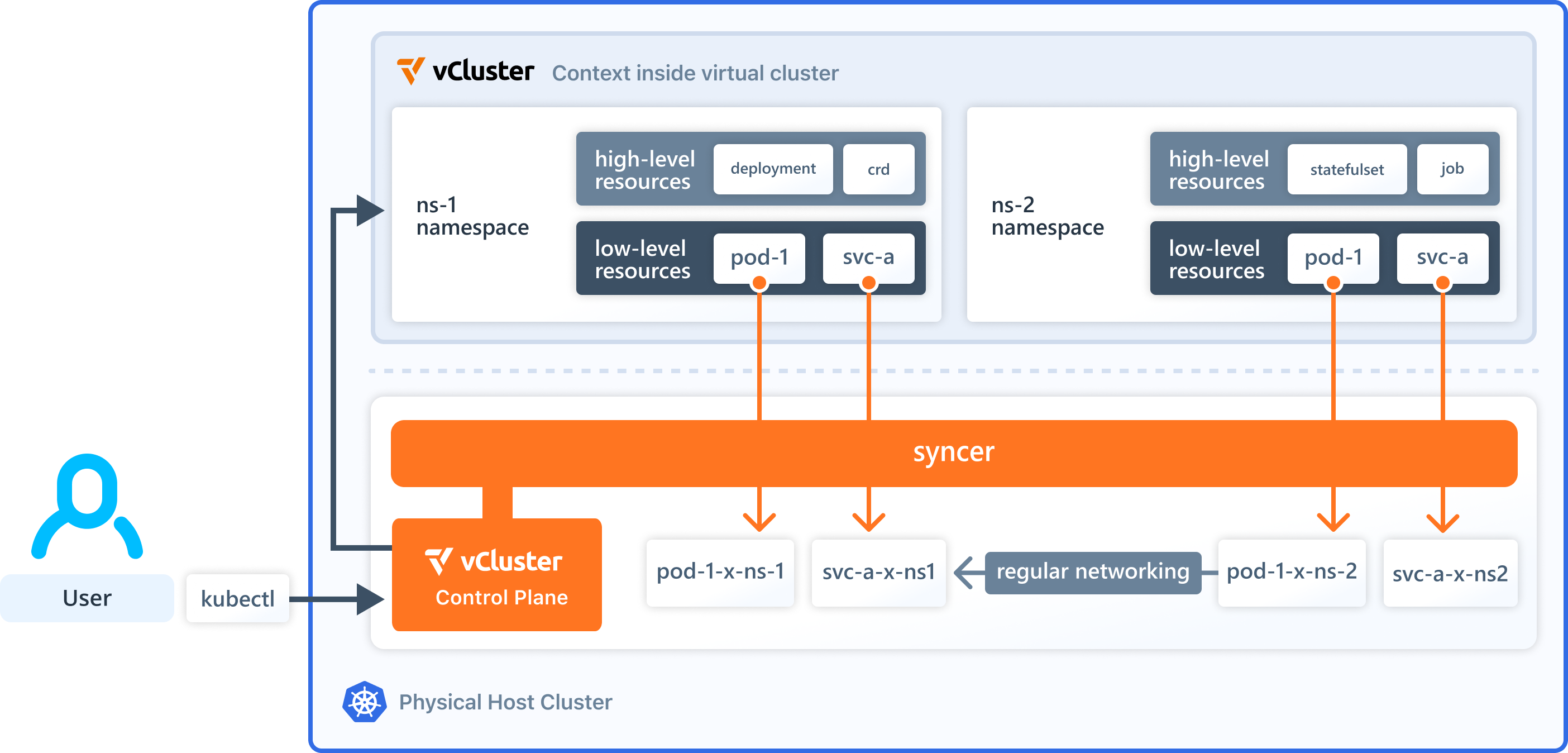
Key Features of vCluster
- Isolation: Each virtual cluster has its own control plane, enhancing security and minimizing conflicts among teams.
- Resource Management: Virtual clusters manage their resources independently, allowing for efficient scaling and resource utilization.
- Multi-Tenancy: Supports multiple teams or tenants operating within the same physical infrastructure without interference.
- Flexibility: Can run on various Kubernetes distributions and supports different backing stores for data management.
Relationship Between Kubernetes and vCluster
- Foundation: vCluster is built on top of Kubernetes, leveraging its capabilities to provide additional layers of abstraction and isolation.
- Resource Sharing: While vClusters share the physical resources of the host Kubernetes cluster, they maintain operational independence, allowing teams to work without affecting the global state of the host cluster.
- Enhanced Security: vClusters provide granular permissions and isolated control planes, which enhance security compared to standard Kubernetes namespaces.
- Operational Efficiency: By reducing the load on the host cluster’s API server and allowing independent management of resources, vClusters improve overall operational efficiency.